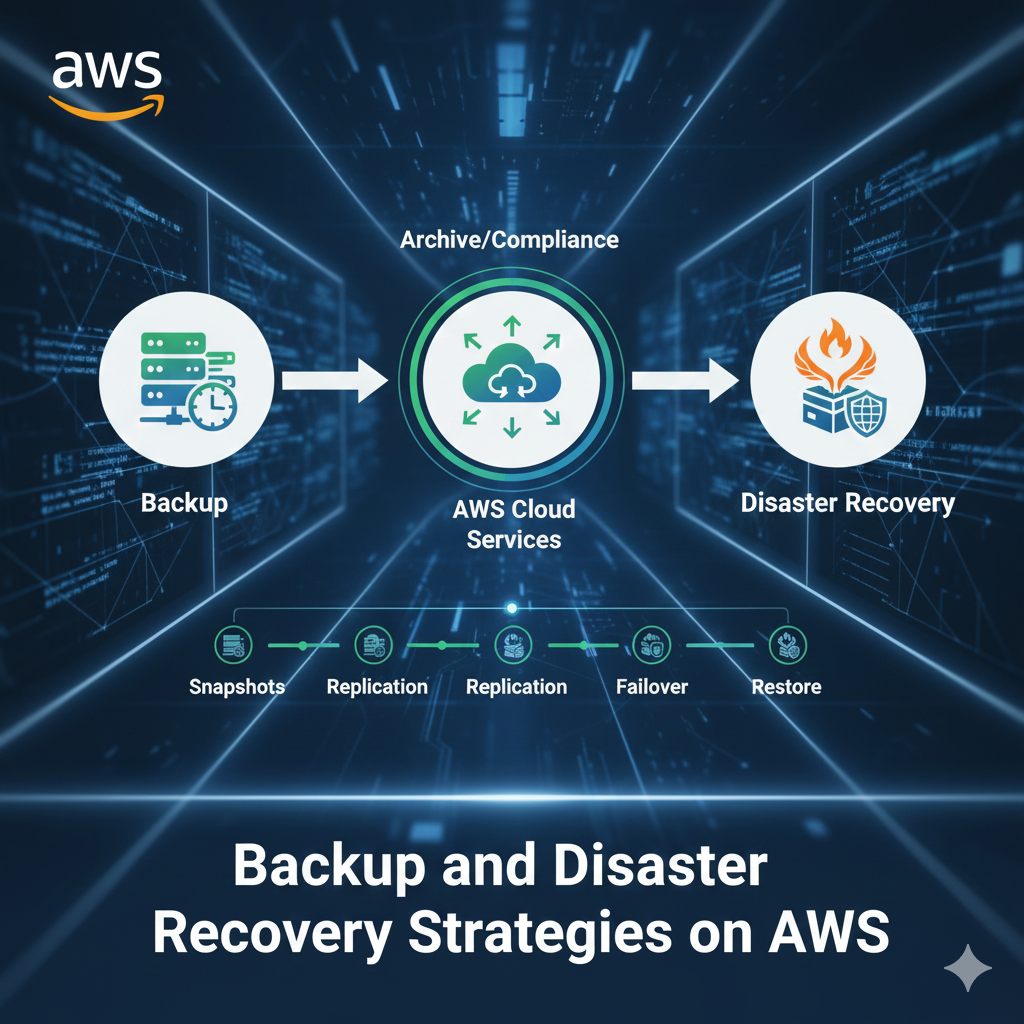
Why Backup and Disaster Recovery Matter in the Cloud
Despite AWS’s robust infrastructure, implementing comprehensive backup and disaster recovery (DR) strategies remains critical for business continuity. Data loss can occur due to human error, malicious attacks, application bugs, or regional outages.
Understanding AWS Backup and Recovery Fundamentals
AWS provides multiple layers of protection and recovery options, from simple snapshots to complex multi-region disaster recovery architectures.
Key Backup Concepts
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): How quickly you need to recover
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): How much data loss is acceptable
- Backup frequency: How often backups are created
- Retention policies: How long backups are stored
AWS Backup: Centralized Backup Management
AWS Backup is a fully managed service that centralizes and automates backup across AWS services.
Supported AWS Services
- Amazon EC2 instances and EBS volumes
- Amazon RDS databases
- Amazon DynamoDB tables
- Amazon EFS file systems
- Amazon S3 buckets
- AWS Storage Gateway volumes
Setting Up AWS Backup
Create backup plans with retention rules, lifecycle policies, and recovery point objectives. Apply backup plans to resources using tags or resource IDs for automated protection.
EBS Snapshot Strategies
Amazon EBS snapshots provide point-in-time copies of your volumes stored in Amazon S3.
Best Practices for EBS Snapshots
- Schedule regular automated snapshots
- Use Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM) for automation
- Copy snapshots across regions for disaster recovery
- Tag snapshots for easy identification and management
- Test restoration regularly
Incremental Snapshots
EBS snapshots are incremental, meaning only changed blocks are saved after the initial snapshot, reducing storage costs and backup time.
RDS Automated Backups and Snapshots
Amazon RDS provides two backup methods: automated backups and manual snapshots.
Automated Backups
- Daily full backups during backup window
- Transaction logs for point-in-time recovery
- Retention period from 1 to 35 days
- Automatic deletion when RDS instance is deleted
Manual Snapshots
- User-initiated snapshots retained indefinitely
- Can be shared across AWS accounts
- Useful for pre-deployment backups
- No automatic deletion
S3 Versioning and Cross-Region Replication
Amazon S3 provides multiple data protection mechanisms for object storage.
S3 Versioning
Enable versioning to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object. This protects against accidental deletions and overwrites.
Cross-Region Replication (CRR)
Automatically replicate objects across AWS regions for disaster recovery and compliance requirements.
S3 Lifecycle Policies
Transition older versions to cheaper storage classes like S3 Glacier or S3 Glacier Deep Archive to optimize costs.
Disaster Recovery Architectures on AWS
Backup and Restore (Lowest Cost)
Regular backups stored in S3 or Glacier with manual or automated restoration. Highest RTO and RPO but most cost-effective.
Pilot Light
Minimal core infrastructure always running in DR region. Scale up quickly when disaster strikes. Moderate RTO and cost.
Warm Standby
Scaled-down but fully functional version running in DR region. Quick recovery with moderate ongoing costs.
Multi-Site Active-Active (Highest Cost)
Full production capacity in multiple regions with traffic distribution. Lowest RTO/RPO but highest cost.
DynamoDB Backup and Point-in-Time Recovery
DynamoDB offers two backup methods for table protection.
On-Demand Backups
- Manual backups retained until explicitly deleted
- Full backups stored independently
- No performance impact on tables
- Restore to new tables in any region
Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR)
- Continuous backups for last 35 days
- Restore to any second within recovery window
- Minimal overhead on table performance
- Protects against accidental writes or deletes
Testing Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Regular testing ensures your DR strategy works when needed.
DR Testing Best Practices
- Conduct quarterly DR drills
- Document recovery procedures step-by-step
- Measure actual RTO and RPO against targets
- Update runbooks based on test results
- Train team members on recovery processes
Automating Backup and Recovery with Infrastructure as Code
Use AWS CloudFormation, Terraform, or AWS CDK to automate backup configurations and disaster recovery infrastructure.
Benefits of Automation
- Consistent backup policies across environments
- Version-controlled disaster recovery configurations
- Rapid deployment of DR infrastructure
- Reduced human error
Compliance and Backup Retention Requirements
Different industries have specific backup and retention requirements:
- HIPAA: Minimum 6-year retention for healthcare data
- PCI DSS: One year of audit trail retention
- GDPR: Right to erasure must be balanced with retention
- SOX: 7-year retention for financial records
Cost Optimization for Backup and DR
Balance protection with cost efficiency:
- Use S3 lifecycle policies to transition old backups to Glacier
- Implement backup retention policies to delete obsolete backups
- Compress backups before storage
- Use reserved capacity for DR infrastructure
- Monitor backup storage costs with AWS Cost Explorer
Conclusion: Building a Resilient Backup Strategy
A comprehensive backup and disaster recovery strategy on AWS requires planning, automation, and regular testing. Start by defining your RTO and RPO requirements, then implement appropriate solutions that balance cost with business needs.









Leave a Comment