Planning Your AWS Data Migration Journey
Migrating data to AWS is a critical step in cloud adoption. Whether you’re moving databases, files, or entire applications, proper planning and the right tools ensure a smooth transition with minimal downtime.
Understanding AWS Migration Strategies: The 7 Rs
Rehost (Lift and Shift)
Move applications without modifications. Fastest approach but doesn’t leverage cloud-native benefits.
Replatform (Lift and Reshape)
Make minimal cloud optimizations during migration. Balance between speed and optimization.
Repurchase
Switch to cloud-native alternatives (SaaS). Replace legacy systems with AWS-managed services.
Refactor/Re-architect
Redesign applications to be cloud-native. Highest effort but maximum cloud benefits.
Retire
Decommission applications no longer needed. Reduces migration scope and costs.
Retain
Keep applications on-premises temporarily. Migrate later when ready.
Relocate
Move infrastructure to AWS without modifications (VMware Cloud on AWS).
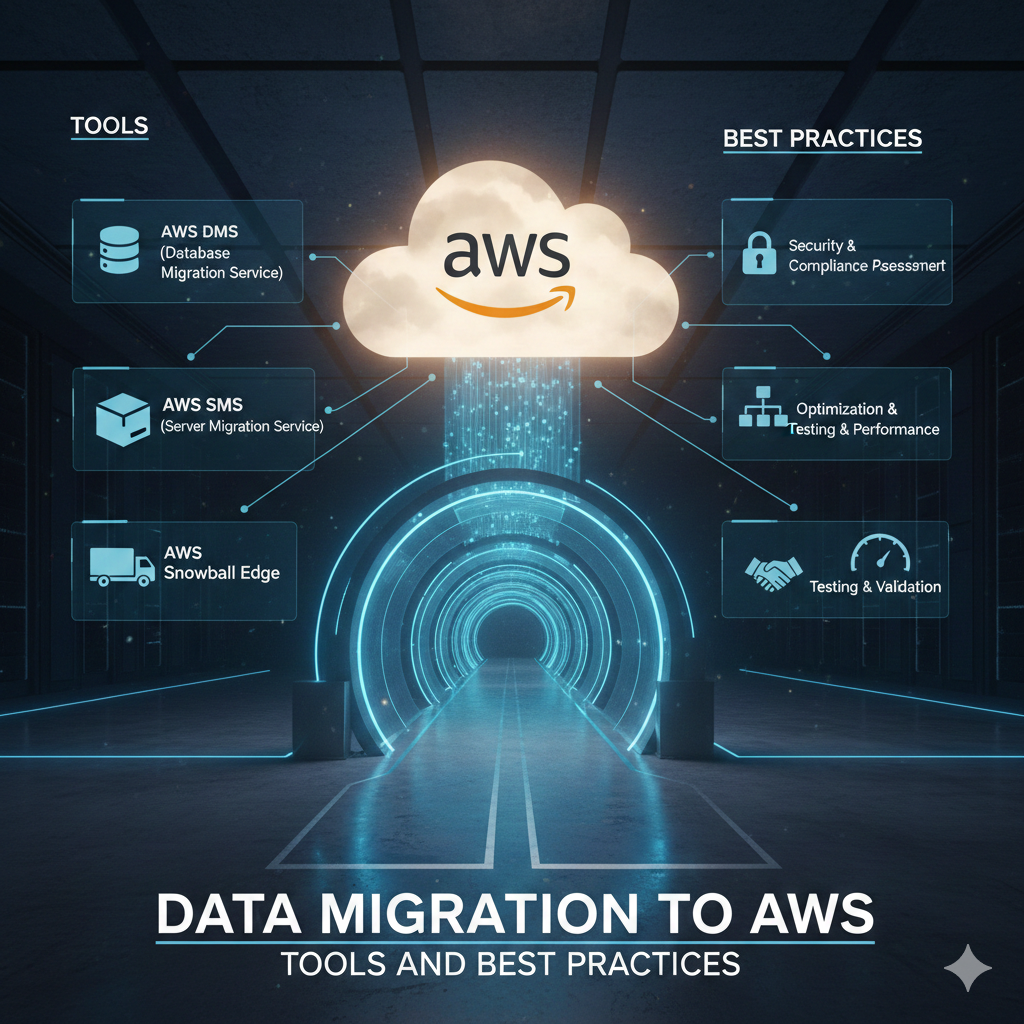
AWS Data Migration Tools Overview
AWS offers a comprehensive suite of migration tools for different scenarios.
AWS Application Discovery Service
Discover on-premises infrastructure and application dependencies before migration. Provides insights into:
- Server specifications and utilization
- Network dependencies
- Application performance metrics
- Cost estimates for AWS
AWS Migration Hub
Central location to track migration progress across multiple AWS and partner tools. Provides unified view of migration status and automates progress tracking.
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
DMS helps migrate databases to AWS with minimal downtime.
Key Features of AWS DMS
- Supports homogeneous migrations (Oracle to Oracle)
- Supports heterogeneous migrations (Oracle to Aurora)
- Continuous data replication
- Minimal downtime during migration
- Automatic schema conversion with AWS SCT
Supported Database Sources
- Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB
- SAP ASE, IBM Db2
- Azure SQL Database
- Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Amazon S3
DMS Migration Process
- Create replication instance in AWS
- Configure source and target endpoints
- Create migration task with table mappings
- Start migration and monitor progress
- Perform validation and cutover
AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT)
AWS SCT converts database schemas and code objects when migrating between different database engines.
SCT Capabilities
- Automated schema conversion
- Application code conversion (SQL, stored procedures)
- Database assessment reports
- Compatibility analysis
- Optimization recommendations
Common Conversion Scenarios
- Oracle to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL
- SQL Server to Amazon RDS for MySQL
- Teradata to Amazon Redshift
- Oracle to Amazon Redshift
AWS DataSync for File Transfers
AWS DataSync automates and accelerates moving data between on-premises storage and AWS.
DataSync Features
- Up to 10x faster than open-source tools
- Built-in data validation
- Bandwidth throttling
- Encryption in transit
- Support for NFS, SMB, HDFS, and S3
Use Cases for DataSync
- Data migration to AWS
- Ongoing data replication
- Archiving cold data to S3 Glacier
- Data processing workflows
AWS Snow Family for Large-Scale Data Transfer
When network transfer isn’t practical, AWS Snow devices provide physical data transport.
AWS Snowcone
- 8 TB of storage
- Portable and rugged
- Edge computing capabilities
- Ideal for remote locations
AWS Snowball
- 80 TB storage capacity
- Faster data transfer than internet
- Tamper-resistant and encrypted
- Good for datacenter migrations
AWS Snowmobile
- Up to 100 PB per Snowmobile
- Exabyte-scale data transfer
- For massive datacenter migrations
- Dedicated migration specialists
AWS Transfer Family for SFTP/FTPS/FTP
Managed file transfer service that enables SFTP, FTPS, and FTP access to Amazon S3 or EFS.
Transfer Family Benefits
- Fully managed service
- No infrastructure to maintain
- Integrates with existing authentication systems
- High availability and scalability
- Pay-per-use pricing
Database Migration Best Practices
Pre-Migration Assessment
- Analyze database size and complexity
- Identify dependencies and integrations
- Estimate migration timeline
- Calculate network bandwidth requirements
During Migration
- Use DMS test mode to validate
- Monitor replication lag
- Implement validation checks
- Maintain transaction logs
Post-Migration
- Verify data integrity
- Update connection strings
- Monitor application performance
- Optimize for cloud environment
Minimizing Downtime During Migration
Continuous Replication Strategy
- Set up DMS with continuous replication
- Perform initial full load
- Maintain ongoing change data capture (CDC)
- Run parallel testing on target database
- Cut over during maintenance window
Multi-Phase Migration
- Migrate non-critical data first
- Test thoroughly before critical data
- Stagger migration to reduce risk
- Keep rollback plan ready
Data Migration Security Considerations
Encryption Requirements
- Encrypt data in transit using TLS/SSL
- Encrypt data at rest using AWS KMS
- Use VPN or AWS Direct Connect for sensitive data
- Implement IAM roles with least privilege
Compliance During Migration
- Maintain audit logs
- Ensure regulatory compliance (HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS)
- Data residency requirements
- Chain of custody documentation
Network Optimization for Data Transfer
Bandwidth Considerations
- Calculate required bandwidth: (Data Size / Available Time Window)
- Consider AWS Direct Connect for large transfers
- Use DataSync bandwidth throttling
- Schedule transfers during off-peak hours
Accelerating Transfers
- Use AWS DataSync acceleration
- Enable S3 Transfer Acceleration
- Compress data before transfer
- Parallelize transfers when possible
Post-Migration Optimization
Performance Tuning
- Right-size resources based on actual usage
- Implement caching strategies
- Optimize database queries
- Use CloudWatch for monitoring
Cost Optimization
- Analyze resource utilization
- Implement auto-scaling
- Use Reserved Instances or Savings Plans
- Archive infrequently accessed data to cheaper storage tiers
Common Migration Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Large Data Volumes
Solution: Use AWS Snow devices or multi-stage migration with compression
Challenge: Minimal Downtime Requirements
Solution: Implement continuous replication with DMS and plan maintenance window cutover
Challenge: Complex Database Dependencies
Solution: Use Application Discovery Service and detailed dependency mapping
Challenge: Heterogeneous Database Migration
Solution: Use AWS SCT for schema conversion and extensive testing
Conclusion: Successful Data Migration Strategy
Successful AWS data migration requires careful planning, the right tools, and thorough testing. Start with a pilot migration, document lessons learned, and scale your approach for full production migration.









Leave a Comment